Menopausal problems
Menopause occurs when a woman hasn’t menstruated in 12 consecutive months and can no longer become pregnant naturally. It usually begins between the ages of 45 and 55, but can develop before or after this age range. Menopause can cause uncomfortable symptoms, such as hot flashes and weight gain. For most women, medical treatment isn’t needed for menopause.
|
Most women first begin developing menopause symptoms about four years before their last period. Symptoms often continue until about four years after a woman’s last period. A small number of women experience menopause symptoms for up to a decade before menopause actually occurs, and 1 in 10 women experience menopausal symptoms for 12 years following their last period. The median age for menopause is 51, though it may occur on average up to two years earlier for African-American and Latina women. More studies are needed to understand the onset of menopause for non-Caucasian women. There are many factors that help determine when you’ll begin menopause, including genetics and ovary health. Perimenopause occurs before menopause. Perimenopause is a time when your hormones begin to change in preparation for menopause. It can last anywhere from a few months to several years. Many women begin perimenopause some point after their mid-40s. Other women skip perimenopause and enter menopause suddenly. About 1 percent of women begin menopause before the age of 40, which is called premature menopause or primary ovarian insufficiency. About 5 percent of women undergo menopause between the ages of 40 and 45. This is referred to as early menopause. |
Perimenopause vs. menopause vs. postmenopauseDuring perimenopause, menstrual periods become irregular. Your periods may be late, or you may completely skip one or more periods. Menstrual flow may also become heavier or lighter. Menopause is defined as a lack of menstruation for one full year. Postmenopause refers to the years after menopause has occurred. Every woman’s menopause experience is unique. Symptoms are usually more severe when menopause occurs suddenly or over a shorter period of time. Conditions that impact the health of the ovary, like cancer or hysterectomy, or certain lifestyle choices, like smoking, tend to increase the severity and duration of symptoms. Aside from menstruation changes, the symptoms of perimenopause, menopause, and postmenopause are generally the same. The most common early signs of perimenopause are:
An estimated 75 percent of women experience hot flashes with menopause. Other common symptoms of menopause include:
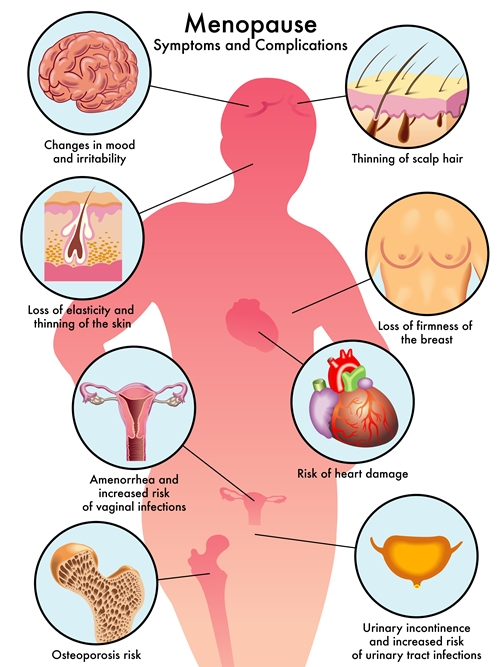
Common complications of menopause include:
Menopause is a natural process that occurs as the ovaries age and produce less reproductive hormones. The body begins to undergo several changes in response to lower levels of:
One of the most notable changes is the loss of active ovarian follicles. Ovarian follicles are the structures that produce and release eggs from the ovary wall, allowing menstruation and fertility. Most women first notice the frequency of their period becoming less consistent, as the flow becomes heavier and longer. This usually occurs at some point in the mid-to-late 40s. By the age of 52, most U.S. women have undergone menopause. In some cases, menopause is induced, or caused by injury or surgical removal of the ovaries and related pelvic structures. Common causes of induced menopause include:
|
| Herbal remedies for menopausal problems | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|








125.jpg)
