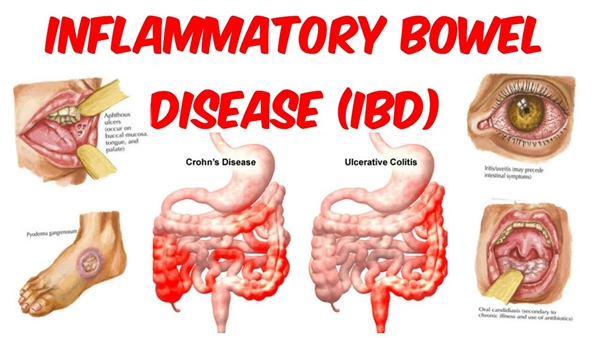
Symptoms
Inflammatory bowel disease symptoms
vary, depending on the severity of
inflammation and where it occurs.
Symptoms may range from mild to severe.
You are likely to have periods of active
illness followed by periods of
remission.
Signs and symptoms that are common to
both Crohn's disease and ulcerative
colitis include:
-
Diarrhea
-
Fever and fatigue
-
Abdominal pain and cramping
-
Blood in your stool
-
Reduced appetite
-
Unintended weight loss
Causes
The exact cause of inflammatory bowel
disease remains unknown. Previously,
diet and stress were suspected, but now
doctors know that these factors may
aggravate but don't cause IBD.
One possible cause is an immune system
malfunction. When your immune system
tries to fight off an invading virus or
bacterium, an abnormal immune response
causes the immune system to attack the
cells in the digestive tract, too.
Heredity also seems to play a role in
that IBD is more common in people who
have family members with the disease.
However, most people with IBD don't have
this family history.
Risk factors
-
Age. Most
people who develop IBD are diagnosed
before they're 30 years old. But
some people don't develop the
disease until their 50s or 60s.
-
Race or ethnicity. Although
whites have the highest risk of the
disease, it can occur in any race.
If you're of Ashkenazi Jewish
descent, your risk is even higher.
-
Family history. You're
at higher risk if you have a close
relative — such as a parent, sibling
or child — with the disease.
-
Cigarette smoking. Cigarette
smoking is the most important
controllable risk factor for
developing Crohn's disease. Although
smoking may provide some protection
against ulcerative colitis, the
overall health benefits of not
smoking make it important to try to
quit.
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory
medications. These
include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB,
others), naproxen sodium (Aleve),
diclofenac sodium (Voltaren) and
others. These medications may
increase the risk of developing IBD
or worsen disease in people who have
IBD.
-
Where you live. If
you live in an industrialized
country, you're more likely to
develop IBD. Therefore, it may be
that environmental factors,
including a diet high in fat or
refined foods, play a role. People
living in northern climates also
seem to be at greater risk.
|