Cardiac arrhythmia
An arrhythmia describes an irregular heartbeat - the heart may beat too fast, too slowly, too early, or irregularly.
Arrhythmias occur when the electrical signals to the heart that coordinate heartbeats are not working properly. For instance, some people experience irregular heartbeats, which may feel like a racing heart or fluttering. Many heart arrhythmias are harmless; however, if they are particularly abnormal, or result from a weak or damaged heart, arrhythmias can cause serious and even potentially fatal symptoms
Fast facts on arrhythmias:
|
||
|
Any interruption to the electrical impulses that cause the heart to contract can result in arrhythmia. For a person with a healthy heart, they should have a heart rate of between 60-100 beats per minute when resting. The more fit a person is, the lower their resting heart rate. Olympic athletes, for example, will usually have a resting heart rate of under 60 beats per minute because their hearts are very efficient. A number of factors can cause the heart to work incorrectly, they include:
A healthy person will hardly ever suffer from long-term arrhythmia unless they have an external trigger, such as drug abuse or an electric shock. If there is an underlying problem, however, the electrical impulses may not be able to travel through the heart correctly, increasing the likelihood of arrhythmia. |
||
|
Some patients have no symptoms, but a doctor might detect an arrhythmia during a routine examination or on an EKG. Even if a patient notices symptoms, it does not necessarily mean there is a serious problem; for instance, some patients with life-threatening arrhythmias may have no symptoms while others with symptoms may not have a serious problem. Symptoms depend on the type of arrhythmia; we will explain the most common below: Symptoms of tachycardiaTachycardia is when the heart beats quicker than normal; symptoms include:
Symptoms of bradycardiaBradycardia is when the heart beats slower than normal; symptoms include:
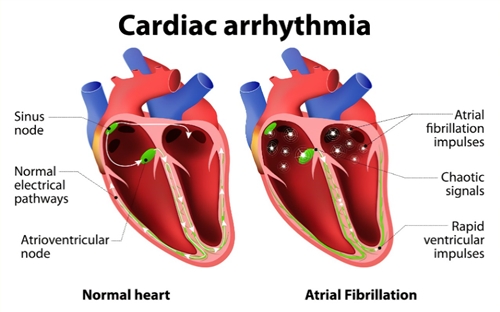
Symptoms of atrial fibrillationAtrial fibrillation is when the upper chambers of the heart beat in an irregular pattern and out of synchrony with the lower chambers. Symptoms often develop rapidly, although sometimes, there are no symptoms:
|
||
|
| Herbal remedies that help with Cardiac arrhythmia | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|






