Breast cancer
What is breast cancer?
Breast cancer starts in the cells of the breast. A cancerous (malignant) tumour is a group of cancer cells that can grow into and destroy nearby tissue. It can also spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body.
Cells in the breast sometimes change and no longer grow or behave normally. These changes may lead to non-cancerous (benign) breast conditions such as atypical hyperplasia and cysts. They can also lead to non-cancerous tumours such as intraductal papillomas.
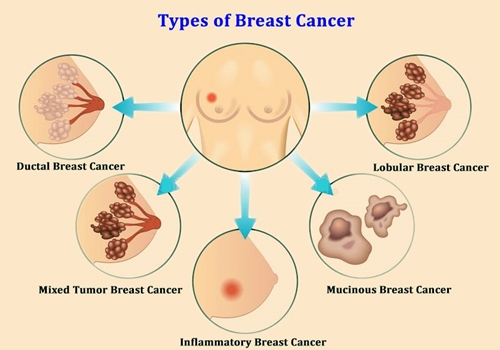
But in some cases, changes to breast cells can cause breast cancer. Most often, breast cancer starts in cells that line the ducts, which are the tubes that carry milk from the glands to the nipple. This type of breast cancer is called ductal carcinoma. Cancer can also start in the cells of the lobules, which are the groups of glands that make milk. This type of cancer is called lobular carcinoma. Both ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma can be in situ, which means that the cancer is still where it started and has not grown into surrounding tissues. They can also be invasive, which means they have grown into surrounding tissues.
Less common types of breast cancer can also develop. These include inflammatory breast cancer, Paget disease of the breast and triple negative breast cancer. Rare types of breast cancer include non-Hodgkin lymphoma and soft tissue sarcoma.
Symptoms of breast cancerBreast cancer may not cause any signs or symptoms in its early stages. Signs and symptoms often appear when the tumour grows large enough to be felt as a lump in the breast or when the cancer spreads to surrounding tissues and organs. Other health conditions can cause the same symptoms as breast cancer. The most common symptom of ductal carcinoma is a firm or hard lump that feels very different from the rest of the breast. It may feel like it is attached to the skin or the surrounding breast tissue. The lump doesn’t get smaller or come and go with your period. It may be tender, but it’s usually not painful. (Pain is more often a symptom of a non-cancerous condition). Lobular carcinoma often does not form a lump. It feels more like the tissue in the breast is getting thicker or harder. |
|
Other symptoms of ductal and lobular breast cancer include:
Late signs and symptoms occur as the cancer grows larger or spreads to other parts of the body, including other organs. Late symptoms of breast cancer include:
Inflammatory breast cancer and Paget disease of the breast cause different symptoms. Inflammatory breast cancer is an an aggressive and fast growing breast cancer in which cancer cells infiltrate the skin and lymph vessels of the breast. It often produces no distinct tumor or lump that can be felt and isolated within the breast. But when the lymph vessels become blocked by the breast cancer cells, symptoms begin to appear.Early IBC symptoms may include persistent itching and the appearance of a rash or small irritation similar to an insect bite. The breast typically becomes red, swollen, and warm. The skin may appear pitted like an orange peel, and nipple changes such as inversion, flattening, or dimpling may occur. Paget's disease of the breast is a type of cancer that outwardly may have the appearance of eczema, with skin changes involving the nipple of the breast. The condition is an uncommon disease accounting for 1 to 4.3% of all breast cancers and was first described by Sir James Paget in 1874. The condition in itself often appears innocuous, limited to a surface appearance and it is sometimes dismissed, although actually indicative of underlying breast cancer. Signs and symptomsPaget's disease of the breast can affect the nipple and areola. Symptoms typically only affect one breast. Symptoms may include:
The symptoms usually affect the nipple and then spread to the areola and then the breast. It is common for the symptoms to wax and wane. Most women do not visit the doctor because they assume Paget's disease to be minor contact dermatitis or eczema. A lump or skin irritation that does not seem to heal for over a month indicates that attention by a specialist is needed. SEE YOUR DOCTOR. |
| Herbal remedies that may help with Breast cancer | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|




